Polyvagal Theory shows how your nervous system shifts between feeling safe, alert, or shut down, directly influencing your emotions and social interactions. When you recognize your body’s signals, like a racing heart or numbness, you can better manage stress and foster connection. Your vagus nerve plays a key role in calming or activating these states. Keep exploring, and you’ll discover practical ways to strengthen your sense of safety and resilience.
Key Takeaways
- Polyvagal Theory explains how the vagus nerve influences emotional regulation, social connection, and physiological states like safety and danger.
- The nervous system shifts between three main states: ventral vagal (calm), sympathetic (alert/fight-or-flight), and dorsal vagal (shutdown).
- Recognizing bodily sensations and emotional cues helps identify current nervous system states and promotes self-regulation.
- Safety signals like calm voice and relaxed body activate social engagement and calm the nervous system.
- Practices such as mindful breathing and gentle social cues strengthen nervous system resilience and emotional well-being.
The Foundations of Polyvagal Theory

What exactly is the foundation of Polyvagal Theory? It’s rooted in understanding how your nervous system adapts through neuroplasticity. This adaptation means your body can rewire itself based on experiences, shaping how you respond to stress and safety cues. neuroplasticity allows your nervous system to change over time, emphasizing that your responses are not fixed. Additionally, the role of the vagus nerve** highlights the importance of parasympathetic pathways in emotional regulation and social connection. Recognizing the various types of nerve pathways provides insight into how these responses are mediated within your nervous system. By recognizing neuroplasticity, you see that your nervous system isn’t fixed; it can change over time. This understanding underpins the idea that you can actively influence your responses, promoting resilience and well-being. Moreover, understanding the adaptive capacity** of your nervous system underscores its ability to recover from stress and trauma. Basically, the foundation of the theory is that your nervous system’s capacity for neuroplasticity adaptation is central to how you navigate the world.
The Three Main States of the Nervous System
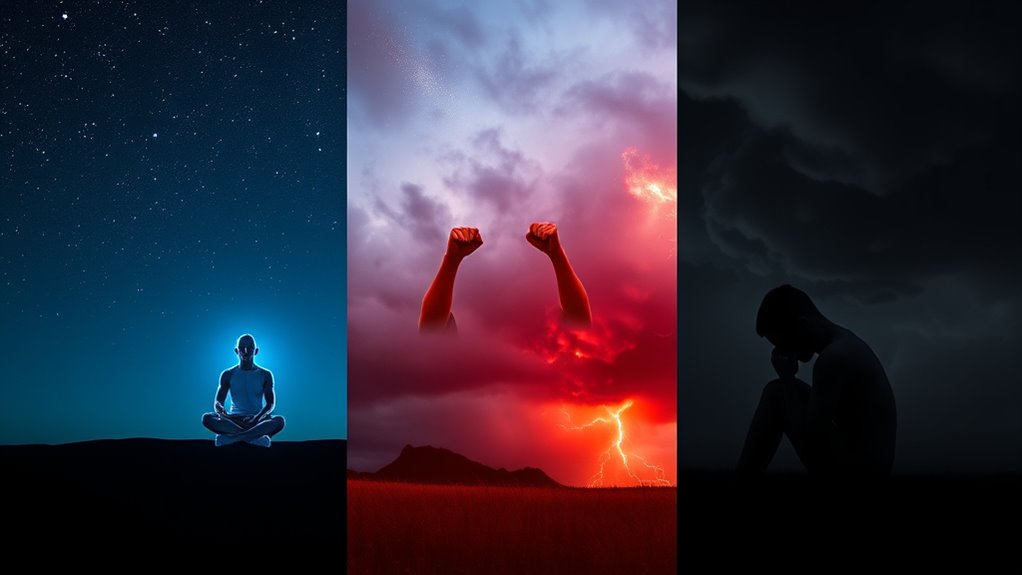

Your nervous system operates primarily in three distinct states, each shaping how you feel, think, and respond to your environment. These states are linked to different autonomic responses and emotional states. The first is the ventral vagal state, where you feel safe, connected, and calm. Your body promotes social engagement and relaxation, which is essential for homeostasis and overall well-being. Next is the sympathetic state, which triggers fight-or-flight responses—your heart races, muscles tense, and you feel alert or anxious. Biological factors influence how easily you shift into this state. Finally, there’s the dorsal vagal state, often called shutdown; it leads to feelings of numbness, disconnection, or helplessness. Recognizing these states helps you understand your emotional reactions and bodily responses. Becoming aware of which state you’re in can help you regulate your responses, and you can start to move toward feeling more balanced and secure. Understanding the nervous system’s different states can empower you to manage stress more effectively and promote overall well-being.
How Your Body Detects Safety and Danger

When your nervous system shifts between states, it’s constantly scanning your environment for signs of safety or danger. This threat detection relies on your body recognizing safety cues, like calm voices or relaxed body language, which signal safety. Conversely, it detects danger through cues like loud noises, aggressive gestures, or tense environments. Your body’s sensory systems—sight, sound, touch—work together to assess these signals quickly. When safety cues are present, your nervous system relaxes, promoting social engagement and calmness. But if threat detection picks up danger signals, your system prepares a response, such as increased heart rate or muscle tension. This ongoing process helps you react appropriately, either by approaching safety or preparing for defense, ensuring your survival and emotional well-being. Recognizing these cues is essential for understanding how narcissistic behaviors can trigger protective responses in individuals. Additionally, understanding the role of the nervous system in this process can help foster better emotional regulation and social connection. The body’s ability to rapidly interpret these signals is supported by sensory integration, which enables a cohesive response to complex environmental cues.
The Vagus Nerve and Its Role in Regulation
Have you ever wondered how your body maintains balance between alertness and calmness? That’s where the vagus nerve plays an essential role. It’s the longest cranial nerve, connecting your brain to your heart, lungs, and digestive system. When activated through parasympathetic activation, the vagus nerve helps slow your heart rate, promotes relaxation, and supports digestion. It acts as a brake on your stress response, encouraging a state of calm. This nerve sends signals that regulate your overall nervous system, helping you switch smoothly between feeling safe and alert. By understanding how the vagus nerve works, you can better harness its power to manage stress and foster emotional resilience. It also plays a key role in mental clarity and health, supporting cognitive function and emotional stability. Its role in regulation is critical for maintaining your physical and mental well-being, especially considering how vulnerable our systems are to AI vulnerabilities and biases. Recognizing its importance can enhance your understanding of Special Occasions and how they influence emotional and physiological states. Additionally, engaging in practices such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and parasympathetic activation can stimulate the vagus nerve and improve overall nervous system regulation.
Recognizing Your Nervous System’s Signals

The signals from your nervous system often manifest as physical sensations or emotional cues, providing valuable clues about your current state. You might notice a racing heart, tightness in your chest, or a sense of numbness. Emotional cues such as feeling anxious, calm, or disconnected can also reveal your body’s response. Paying attention to these bodily sensations helps you identify whether you’re in a state of safety, danger, or alertness. For example, shallow breathing or muscle tension may signal stress, while relaxed muscles and steady breathing indicate calmness. Recognizing these signals allows you to become more aware of your nervous system’s activity, empowering you to respond intentionally. Developing an awareness of your bodily sensations can also help you distinguish between different nervous system states more effectively. Additionally, understanding expert advice about your body’s responses can deepen your awareness and enhance your self-regulation strategies. Cultivating this awareness is essential for nervous system regulation and overall well-being. Incorporating mindfulness techniques can further enhance your perception of these signals, making it easier to respond appropriately. Exploring practices like meditation and deep breathing can further support autonomic nervous system balance, promoting a state of calm and resilience.
Practical Ways to Engage Your Social Engagement System

You can activate your social engagement system by making intentional eye contact, which helps build connection and trust. Gentle touches, like a reassuring pat, can also signal safety to your nervous system. Additionally, speaking in warm, calm tones encourages a sense of calm and openness in others.
Deepen Eye Contact
Deepening eye contact can be a powerful way to activate your social engagement system, helping you feel more connected and grounded in social interactions. Eye contact, as a key nonverbal cue, communicates trust, attention, and openness. When you consciously extend your gaze, you invite others into a shared space of connection, signaling safety and engagement. Focus on softening your gaze and maintaining gentle eye contact without staring, which can feel intimidating. This practice encourages mutual understanding and creates a sense of presence. Remember, subtle cues matter:
- Maintain steady but relaxed eye contact
- Observe the other person’s nonverbal signals
- Use eye contact to show genuine interest
- Avoid darting or overly intense gazes
- Balance eye contact with occasional breaks for comfort
These small shifts can deepen your social engagement and foster trust.
Use Calming Touch
Introducing calming touch as a practical way to activate your social engagement system can help you feel more connected and safe in interactions. Gentle, soothing gestures like light touches on the arm or shoulder can signal safety and foster trust. When you use calming touch intentionally, you send cues to your nervous system that it’s okay to relax. These touches don’t need to be elaborate—simple, consistent gestures work best. Remember, the goal is to create a sense of comfort and connection, so pay attention to the other person’s response. Calming touch can help shift your nervous system from a state of alertness to one of safety, making social interactions more easeful and genuine. Practice with kindness, and notice how it enhances your connection.
Practice Vocal Warmth
Practicing vocal warmth involves using a gentle, inviting tone to foster a sense of safety and connection in your interactions. When you intentionally soften your voice and add emotional expression, you signal safety to others, encouraging openness. This helps activate your social engagement system and promotes trust.
To enhance vocal warmth:
- Use a calm, steady voice that conveys reassurance
- Incorporate subtle variations in pitch for emotional depth
- Speak slowly to allow others to process your message
- Maintain eye contact and relaxed facial expressions
- Practice active listening to respond authentically
Applying Polyvagal Principles to Improve Well-Being

Applying polyvagal principles can substantially enhance your overall well-being by helping you better understand and regulate your body’s responses to stress and safety cues. One effective way is through mindful breathing, which calms your nervous system and shifts you from a state of alarm to safety. Practicing emotional awareness allows you to recognize your feelings without judgment, helping you stay connected to your body’s signals. By tuning into these cues, you can consciously choose strategies that promote relaxation and social engagement, fostering resilience. Incorporating simple practices like deep, intentional breaths and observing your emotional states empowers you to manage stress more effectively. Over time, this awareness and regulation strengthen your nervous system, leading to improved mental and physical health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Polyvagal Theory Relate to Mental Health Treatments?
You might wonder how mental health treatments work. Polyvagal Theory explains that understanding your nervous system helps improve emotional regulation. Therapists often use techniques grounded in this theory to help you recognize and shift between states of safety and danger. By doing so, you can better manage stress, anxiety, and trauma, making therapy more effective. This approach encourages a deeper connection to your body, promoting healing and resilience.
Can Polyvagal Strategies Help With Chronic Pain Management?
You can use polyvagal strategies to help manage chronic pain by promoting pain relief and emotional regulation. When you activate your vagus nerve through calming techniques like deep breathing or gentle movement, you signal safety to your nervous system. This can reduce pain perception and help you stay emotionally balanced. By practicing these strategies regularly, you take control, easing your pain and fostering a sense of calm and stability.
Is Polyvagal Theory Applicable Across Different Age Groups?
You might wonder if Polyvagal Theory applies across different age groups. The answer is yes, because it considers age adaptability and developmental differences. As you grow, your nervous system evolves, but the core principles remain relevant. Strategies based on this theory can help you, whether you’re a child, adult, or senior, by promoting safety, regulation, and social engagement, tailored to your specific developmental stage.
How Does Trauma Impact the Functioning of the Vagus Nerve?
Trauma effects can markedly impact the vagus nerve, leading to vagus damage or dysregulation. When you experience trauma, it may cause your vagus nerve to become less effective at calming your nervous system, resulting in heightened stress or anxiety. This damage can hinder your ability to recover from stress and maintain emotional balance. Recognizing these effects helps you understand the importance of healing and supporting your nervous system.
Are There Specific Exercises to Strengthen the Social Engagement System?
You can strengthen your social engagement system through simple exercises. Practice deep, calming breathing exercises to regulate your nervous system and promote relaxation. Incorporate facial expressions like smiling or maintaining eye contact to activate your social engagement cues. Engaging regularly in these activities helps enhance your ability to connect with others, reduces stress, and boosts your overall sense of safety and social confidence.
Conclusion
By understanding your nervous system’s gentle dance between safety and tension, you can guide yourself toward calmer, more connected moments. Embrace these subtle shifts as opportunities to nurture your well-being, like tending to a delicate garden. With patience and awareness, you’ll discover how to softly invite feelings of safety and ease into your daily life. Remember, your body’s natural rhythms are there to support you—trust them and enjoy the gentle flow.









